Gate-Based Spin Readout of Hole Quantum Dots with Site-Dependent -Factors
Published in Physical Review Applied
Angus Russell, Alexander Zotov, Ruichen Zhao, Andrew S Dzurak, M Fernando Gonzalez-Zalba & Alessandro Rossi
Abstract
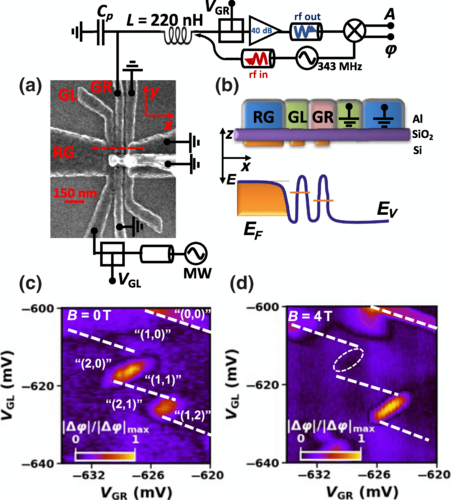
The rapid progress of hole spin qubits in group IV semiconductors has been driven by their potential for scalability. This is due to the compatibility with industrial manufacturing standards, as well as the ease of operation and addressability via all-electric drives. However, owing to a strong spin-orbit interaction, these systems present variability and anisotropy in key qubit control parameters such as the Landé 𝑔-factor, requiring careful characterization for reliable qubit operation. Here, we experimentally investigate a hole double quantum dot in silicon by carrying out spin readout with gate-based reflectometry. We show that characteristic features in the reflected phase signal arising from magnetospectroscopy convey information on site-dependent 𝑔-factors in the two dots. Using analytical modeling, we extract the physical parameters of our system and, through numerical calculations, we extend the results to point to the prospect of conveniently extracting information about the local 𝑔-factors from reflectometry measurements.