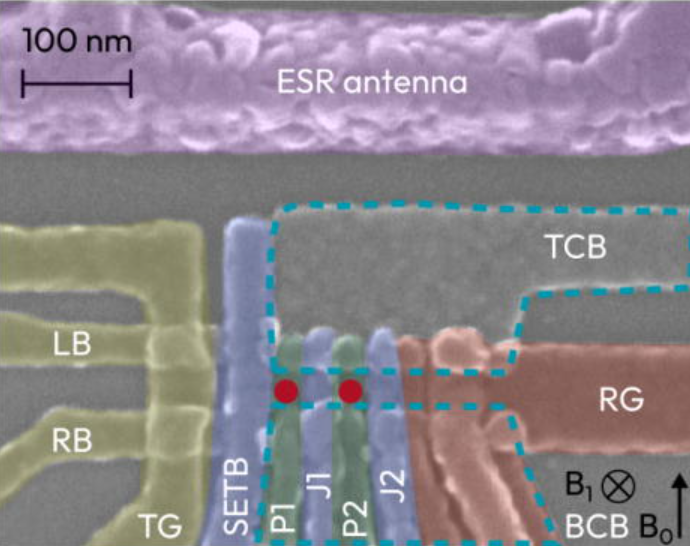
Silicon spin qubit noise characterization using real-time feedback protocols and wavelet analysis
Published in Applied Physics Letters
Nard Dumoulin Stuyck, Amanda E Seedhouse, Santiago Serrano, Tuomo Tanttu, Will Gilbert, Jonathan Yue Huang, Fay Hudson, Kohei M Itoh, Arne Laucht, Wee Han Lim, Chih Hwan Yang, Andre Saraiva, Andrew S Dzurak
Abstract
Recently, several groups have demonstrated two-qubit gate fidelities in semiconductor spin qubit systems above 99%. Achieving this regime of fault-tolerant compatible high fidelities is nontrivial and requires exquisite stability and precise control over the different qubit parameters over an extended period of time. This motivates the search for the efficient calibration of qubit control parameters against different sources of micro-and macroscopic noise and methods for noise analysis. Here, we present several single-and two-qubit parameter feedback protocols, optimized for and implemented in the state-of-the-art fast field-programmable gate array hardware. Furthermore, we present a wavelet-based analysis on feedback data collected over a∼ 9 h time frame to gain insight into the different sources of noise in the system. Scalable feedback is an outstanding challenge and the presented implementation and analysis gives insight into the benefits and drawbacks of qubit parameter feedback, as feedback related overhead increases. This work demonstrates a pathway toward robust qubit parameter feedback and systematic noise analysis, crucial for mitigation strategies toward systematic high-fidelity qubit operation compatible with quantum error correction protocols.